Therapeutics to harness the immune microenvironment in multiple myeloma
Abstract
Multiple myeloma (MM) remains an incurable, genetically heterogeneous disease characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of transformed plasma cells nurtured within a permissive bone marrow (BM) microenvironment. Current therapies leverage the unique biology of MM cells and target the immune microenvironment that drives tumor growth and facilitates immune evasion. Proteasome inhibitors and immunomodulatory drugs were initially introduced to complement and have now supplanted cytotoxic chemotherapy as frontline anti-myeloma agents. Recently, monoclonal antibodies, bispecific antibodies, and chimeric antigen receptor T cells were developed to revamp the immune system to overcome immune suppression and improve patient responses. While current MM therapies have markedly extended patient survival, acquired drug resistance inevitably emerges and drives disease progression. The logical progression for the next generation of MM therapies would be to design and validate agents that prevent and/or overcome acquired resistance to immunotherapies. The complex BM microenvironment promotes resistance to both current anti-myeloma agents and emerging immunotherapies. Myeloma cells are intertwined with a complex BM immune microenvironment that contributes to the development of adaptive drug resistance. Here, we describe recently FDA-approved and investigational anti-myeloma agents that directly or indirectly target the BM microenvironment to prevent or overcome drug resistance. Synergistic effects of anti-myeloma agents may foster the development of rationally-designed drug cocktails that prevent BM-mediated resistance to immunotherapies.
Keywords
MULTIPLE MYELOMA
Multiple myeloma (MM) is described by clonally expanding plasma cells within the bone marrow (BM), monoclonal proteins detected in blood or urine, and end-organ damage[1,2]. Approximately 13% of all hematologic cancers are classified as MM, which is the 2nd most common hematological cancer in high-income and Western countries[3]. In the US in 2021, approximately 34,920 new cases of MM (19,320 men, 15,600 women) were reported[3-6].The lifetime risk of an MM diagnosis is 1 in 125 (0.8%). The annual incidence of MM/100,000 persons is 8.2 cases (Caucasian men), 5.0 cases (Caucasian women), 16.5 cases (African-American men), 12.0 cases (African-American women), 8.2 (Hispanic men), 5.7 (Hispanic women) and 5.0 (Asians/Pacific Islander men), and 3.2 (Asians/Pacific Islander women)[3-6]. Approximately 12,410 deaths from MM (6,840 men, 5,570 women) were expected in 2021[4]. Newly reported cases of MM did not change significantly over the past 10 years, staying in the range of 6.7/100,000 since 2010, while death rates declined slightly, from 3.4/100,000 in 2008 to 3.1/100,000 in 2018[4]. Expected 5-year survival has improved to ~56%[3-6]. Risk factors include obesity, chronic inflammation, exposure to pesticides, organic solvents, and radiation, and inherited genetic variants[6-8].
MM starts as an asymptomatic precursor condition monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) or smoldering multiple myeloma (SMM). Genetic abnormalities, e.g., hyperdiploidy, translocations are already evident in MGUS and SMM[9-11]. While these precursors may exhibit a significant burden of clonal plasma cells, they require additional genetic changes to drive end-organ damage and become MM.
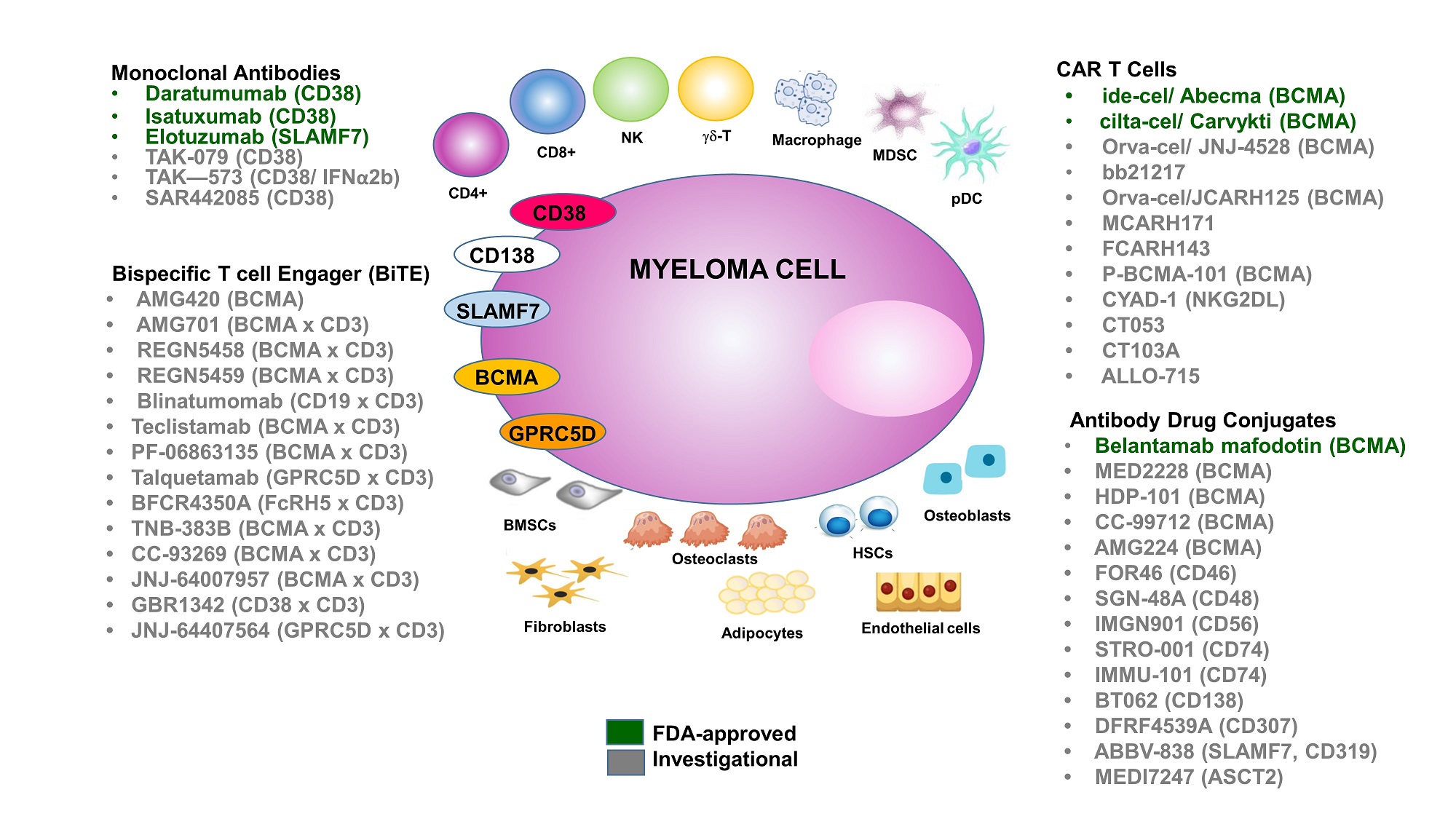
Current MM therapy leverages the unique features of plasma cell biology that proliferate within the BM to promote deep clinical remissions with fewer side effects than cytotoxic chemotherapy. The first FDA-approved proteasome inhibitor (PI) bortezomib, immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) thalidomide, lenalidomide and pomalidomide (Celgene), and monoclonal antibodies that target CD38 and SLAMF7 have significantly extended patient outcome [Table 1][9,12,13]. These FDA-approved agents are used to treat newly diagnosed patients with related next-generation agents exhibiting activity in the relapsed and/or refractory MM (RRMM) in all stages of treatment[9,12,13]. While these agents have markedly improved survival, MM remains incurable, with therapeutic resistance invariably emerging even in patients with an initial favorable response to therapy. Further efforts are needed to define tumor and BM-driven resistance mechanisms to inform next-generation therapies.
Effects of FDA-approved and investigational agents on the myeloma immune microenvironment
| Therapeutic agent | Stage | Target | Effect on myeloma-immune microenvironment |
| Proteasome inhibitors | |||
| Bortezomib (Velcade) | FDA-approved | Proteasome 5 | Bortezomib inhibits osteoclast differentiation induced by the RANKL, stimulates osteoblast differentiation and inhibits autocrine/paracrine signaling in MSCs and in ECM. PIs also reduce MM adhesion to BMSCs[15,16,17,24,33-35] |
| Carfilzomib (Kyprolis) | FDA-approved | Proteasome 5 | |
| Ixazomib (Ninlaro) | FDA-approved | Proteasome 5 | |
| IMiDs | |||
| Thalidomide (Thalomid) | FDA-approved | CRBN | IMiDs promote anti-proliferative, T-cell co-stimulatory, anti-angiogenic and anti-inflammatory effects[38-44] |
| Lenalidomide (Revlimid) | FDA-approved | CRBN | |
| Pomalidomide (Pomalyst) | FDA-approved | CRBN | |
| Cel-MODCC-92480 | Phase 1/2 | CRBN E3 Ub ligase Modulator | Antitumor and immunostimulatory activities |
| CC-220 (Iberdomide) | Phase 1b/2a | CRBN E3 Ub ligase Modulator (CelMOD) | Antitumor and immunostimulatory activities |
| C-92480 (Mezigdomide) | Phase 1/2 | CRBN E3 Ub ligase Modulator (CelMOD) | Antitumor and immunostimulatory activities |
| Monoclonal antibodies | |||
| Daratumumab (Darzalex) | FDA-approved | CD38 | Augments NK-cell cytotoxicity, induces robust increases in helper and cytotoxic T-cell absolute counts. Increases memory T cells while decreasing naïve T cells. Eliminates CD38+ immune suppressor cells, e.g., Tregs, Bregs, and MDSCs[61-69] |
| Elotuzumab (Empliciti) | FDA-approved | SLAMF7 | Induces TAM activation and mediates ADCP through an FcγR-dependent manner in vitro |
| Isatuximab (Sarclisa) | FDA-approved | CD38 | Eliminates CD38+ immunosuppressive Tregs and alleviates BM-induced immunosuppression |
| Nuclear export inhibitors | |||
| Selinexor (Xpovio) | FDA-approved | Exportin 1, (XPO) | Increased NK cell cytotoxicity in vitro, potentiates ADCC, downregulates pro-survival signals from BM microenvironment, blunts the protective effects from pro-survival signals from TNF, IL-6, IL-4, BAFF BMSCs[82-87] |
| Bone-modifying agent | |||
| Denosumab (Prolia) | FDA-approved | RANKL | Potent Inhibitor of osteoclast function[88-90] |
| Bisphosphonates | |||
| Zoledronate (Zometa) | FDA-approved | Farnesyl diphosphate | Reduces osteoclast function, inhibits liberation of matrix-synthase (FDPS) bound cytokines, increases IFN-γ production by IL-2-primed NK cells, decrease tumor cell adhesion to bone, and activates T cells[91-94] |
| CAR T cells | |||
| Idecabtagene vicleucel (ida-cel, Abecma, bb2121) | FDA-approved | TNFRSF17 (BCMA) | T cells are physically recruited and linked to tumor surface Ags to elicit an anti-tumor immune response and overcome BM microenvironment-mediated immunosuppression[95-101] |
| Ciltacabtagene autoleucel (Carvykti, cilta-cel LCAR-B38M, JNJ-4528) | FDA-approved | Two llama-derived Abs that bind human BCMA | Reduce BCMA-cell expression and microenvironment-mediated immunosuppression |
| Bispecific T Cell Engagers | |||
| Blinatumumab (Blincyto) | FDA-Approved (R/R ALL) | CD19-targeting engager (CD19xCD3) | BiTEs bind simultaneously to T cells and tumor Ags, recruits T cells to tumors and tumor T-cell microenvironment, leading to T cell activation, proliferation, and tumor cell death |
| Pilot Study (MM) (NCT03173430) | |||
| Talquetamab | Phase I/II (MM) (NCT03399799) | GPRC5D-targeting bi-specific T-cell engager (GPRC5D x CD3) | Actively kills GPRC5D+ MM cell lines and primary MM cells in vitro[110-115,121] |
| AMG420 (NCT03836053) | Phase 1b (RRMM) | BCMA-targeting bi-specific T-cell engager (BCMA x CD3) | Short half-life with encouraging activity in RRMM. Three patients dosed with 400 µg/d had MRD-negative CRs, 2 more responders in the dose confirmation cohort, 3 patients at lower doses attained CRs. No major toxicities were observed up to 400 µg/d[110-115,122,123] |
| Teclistamab (JNJ-64007957) | Phase 1 (MM) (NCT03145181) | BCMA-targeting bi-specific T-cell engager (BCMA x CD3) | At the phase 2 dose, showed promising efficacy and durable responses, well tolerated[110-115,124] |
MM EFFECTS ON BONE MARROW
Evasion and suppression of antitumor immunity is an essential step in myelomagenesis. MM cells replicate and proliferate nearly exclusively within the BM niche, highlighting the role of the microenvironment in supporting cancer growth[14-16]. The BM microenvironment is highly vascularized and consists of a cellular compartment divided into hematopoietic cells, e.g., hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), T and B lymphocytes, myeloid and natural killer (NK) cells, and osteoclasts. The non-hematopoietic cell types include bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs), osteoblasts, endothelial cells (EC), and fibroblasts[13-16]. The non-cellular compartment consists of an extracellular matrix (ECM), oxygen concentration, and a soluble cocktail milieu of growth factors, cytokines and chemokines. Plasma cell clones traffic in and out of the BM to foster metastatic progression while other cell types re-circulate into and out of the BM to promote cytokine-driven myeloma growth[14-16]. The tumor-immune microenvironment supports the acquisition of resistance to cytotoxic chemotherapy, biologic agents and immunotherapies leading to immune escape[17-20]. Recently it was shown using a pumpless culture platform that adhesion of patient-derived MM cells (PMMCs) to osteoblasts and osteoblast long-term viability were critical factors for ex vivo survival of PMMCs[21]. Osteoblasts can also subvert the anti-myeloma effect of NK cells. Since NK cells (and genetically-engineered chimeric antigen receptor-modified NKs) have clinical potential, a better understanding of the osteoblast role as immune regulators in BM is essential[22]. Similarly, osteoclasts regulate antigen-dependent T cell activation and responses. Like macrophages, monocytes, and dendritic cells (DCs), osteoclasts display phenotypic and functional plasticity that is dependent on their origin and environment[23].
The highly organized BM integrity is disrupted by the invasion of MM cells. A liquid milieu of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and inflammatory mediators mixed with matrix remodeling enzymes enables the communication between tumor, immune and microenvironment cells. Circulating tumor cells, exosomes, cell-free DNA, and apoptotic bodies negotiate the transfer of genetic information from myeloma cells to other tumor and non-tumor cell types[24-29]. Exosomes are small, secreted vesicles that confer the bidirectional transfer of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids between BM and tumor cells. Exosomes can support myelomagenesis by promoting angiogenesis, osteolytic lesions, and drug resistance[17-21]. The content of exosomes from MM patients differs from that of healthy donors and could potentially serve as biomarkers and targets.
MM cells are decorated with adhesion molecules that localize myeloma cells to the ECM[30]. Collagen I, collagen III, and elastin recently were shown to block the cytotoxic effect of NK cells and promote their production of chemokines and cytokines[31]. NK cell cytotoxicity against major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-I-deficient melanoma was markedly increased by blocking tumor collagen deposition. MHC-I down-regulation occurred in solid cancers, which could be directly targeted by circulating cytotoxic NK cells. Prior studies have demonstrated that BMSCs produce paracrine factors and cytokines that drive cell-cell engagement and induce the generation of osteolytic lesions[32-38]. Physical interaction between MM and BMSCs, as well as transforming growth factor (TGF) and interleukin (IL)-6 enhance the formation of lytic bone lesions[32,33]. Cell-cell interactions and cell adhesion also enhance drug resistance in MM cells[33-36]. Unlike healthy mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), myeloma MSCs enhance tumor survival by producing elevated levels of IL-1β and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)[33-39].
PROTEASOME INHIBITORS
Proteasome inhibitors (PIs) are the backbone components of current anti-myeloma regimens[40]. Bortezomib (Millennium-Takeda) demonstrates clinical efficacy and safety for newly diagnosed and RRMM disease. However, the emergence of chemoresistance and the development of adverse effects, especially peripheral neuropathy, can limit clinical utility. Second-generation PIs carfilzomib (Onyx/Amgen) and ixazomib (Millennium-Takeda) are approved for RRMM and may overcome resistance with better tolerability. Bortezomib has received regulatory approval for intravenous and subcutaneous administration, while ixazomib is the only orally bioavailable PI.
PIs also target components of the BM immune microenvironment [Figure 1][40,41]. Kim et al. reported that bortezomib impaired BMSCs proliferation in vitro[41]. PIs downregulate autocrine and paracrine signaling signaled by ECM and MSCs, which impairs myeloma cell growth and survival[14,42]. In addition, PIs suppress interleukin-6 (IL-6), IGF-1, and TNF-α production to decrease CXCL12 production by BMSCs[43,44]. BM angiogenesis also plays an important role in myelomagenesis and suppresses angiogenesis by decreasing VEGF secretion. Roccaro et al. studied MM patient-derived endothelial cells to determine the effects of bortezomib on the angiogenic phenotype[43]. At clinically achievable doses, bortezomib inhibited the proliferation of MM patient endothelial cells as well as human umbilical vein endothelial cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The binding of MM.1S cells to patient-derived endothelial cells augmented the proliferation of myeloma cells, which was abolished by bortezomib. Bortezomib blocked vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and IL-6 secretion by endothelial cells from myeloma patients and reduced VEGF, IL-6, insulin-like growth factor-I, Angiopoietin (Ang1/Ang2) transcription. Taken together, the results illustrate that bortezomib elicits anti-angiogenic effects in BM.
IMMUNOMODULATORY DRUGS
Thalidomide, lenalidomide, and pomalidomide (Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb) are immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) that have contributed to the improvement in MM patient survival[44]. Lenalidomide is employed to treat transplant-eligible and ineligible (NDMM) as maintenance post-transplant and for RRMM. IMiDs are thalidomide analogs, which exhibit pleiotropic anti-myeloma activities such as anti-proliferation, anti-angiogenesis, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory and cytotoxic effects[44-47]. IMiDs also impact the BM microenvironment to lower IL-6 concentrations. Following the introduction of alkylating agents for MM, thalidomide was the next agent to change disease course through VEGF suppression, immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects[44-46]. IMiDs increase T cell and NK cell activity, downregulate cytokines, inhibit bone resorption, and decrease cell adhesion molecules (CAM) to disrupt MM-BMSC interactions and IL-6 production[45-47].
Communication between myeloma cells and other cellular components of the tumor microenvironment, e.g., osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and BMSCs, is bidirectional and highly complex. Lenalidomide downregulates hyperactive osteoclasts and reduces the secretion of osteoclastogenic MIP-1a, B-cell activating factor (BAFF), a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL), and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) ligand (RANK-L)[48,49]. Lenalidomide has also been shown to more significantly decrease TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and interleukin-12 (IL-12) levels and increases interleukin-2 (IL-2) and IFN-γ production compared to thalidomide[50]. LeBlanc et al. found that IMiDs co-stimulated T cells through the B7-CD28 pathway[51]. IMiDs prolonged T cell priming and boosted the uptake of tumor antigens by DCs to improve the efficacy of antigen presentation[52,53]. IMiDs also enhance NK and NK T cell activities[54] and inhibit T regulatory cells (Tregs) proliferation and activity[55]. IMiDs decrease IL-2, IFN-γ, and SOCS1 expression in CD4+ T, CD8+ T, NK+ T, and NK cells from peripheral blood (PB) and B[56].
Programmed death (PD)-1 and PD-ligand-1 (PD-L1) interactions attenuate the production of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) that recognize tumor cells. PD-L1 expression on plasma cells from MM patients is markedly upregulated compared to those from MGUS patients and healthy volunteers[57]. IMiDs downregulate PD-1 levels on T and NK cells and PD-L1 on myeloma cells to promote antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Bortezomib and lenalidomide do not have the flexibility to subdue myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC) activity, whereas CD38-targeting agents do have this capacity[58,59]. Co-stimulatory effects of IMiDs on T and NK cells have been proposed to enhance anti-MM immunity but are yet to be demonstrated in vivo.
MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES
The introduction of PIs and IMiDs represented an initial paradigm shift in MM treatment strategy. Subsequently, in 2015 two monoclonal antibodies were FDA-approved for RRMM treatment and represented a second shift in the treatment approach towards immunotherapies. Daratumumab (Janssen Oncology) is a humanized monoclonal IgG-κ antibody that binds to the transmembrane glycoprotein CD38 (cyclic ADP ribose hydrolase)[60]. CD38 is expressed on immune cells, overexpressed on myeloma cells, and contributes to cell adhesion and ecto-enzymatic activities. Daratumumab binds CD38, causing cells to undergo ADCC, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP). Combination regimens incorporating daratumumab have demonstrated promising results in the relapsed refractory setting and are increasingly used upfront and in transplant-eligible patients[61-64]. Phase III trials showed promising results when daratumumab was combined with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, with bortezomib and dexamethasone, and, in quadruplet therapy with bortezomib, dexamethasone, and lenalidomide[61-64].
Daratumumab also targets CD38+ immune, non-myeloma cell populations. PB and BM were obtained and analyzed before and during therapy and at relapse from RRMM patients enrolled in two daratumumab monotherapy studies[65]. CD38-expressing regulatory B cells (Bregs) and MDSCS were evaluated to determine the effect of daratumumab on immunosuppressive activity. A unique subpopulation of CD38+ Tregs was found to be more immunosuppressive than CD38- Tregs in vitro and was reduced in daratumumab-treated patients. Likewise, daratumumab treatment generated significant elevations in helper and cytotoxic T-cell absolute counts. In PB and BM, daratumumab induced significant increases in CD8+:CD4+ and CD8+:Treg ratios and increased memory T cells while decreasing naïve T cells. The majority of patients demonstrated broad T-cell changes, although patients with a partial response or better showed greater maximum effector and helper T-cell increases. Greater increases in T-cell clonality, measured by T-cell receptor (TCR) sequencing, positively correlated with increased CD8+ PB T-cell counts. Depletion of CD38+ immunosuppressive cells, which is related to a rise in T-helper cells, cytotoxic T cells, T-cell functional response, and TCR clonality, represents an additional mechanism of action for daratumumab and deserves further exploration. The anti-myeloma benefit of daratumumab can be potentiated when combined with bortezomib which leads to increased expression of CD38 target on MM cells. However, daratumumab may also internalize CD38 in MM cells to inhibit adhesion to BMSCs and overcome CAM drug resistance (CAM-DR)[66].
The second humanized monoclonal FDA-approved for MM is elotuzumab (Bristol-Myers Squibb), which binds the signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family 7 (SLAMF7, CD319, cell-surface glycoprotein CD2 subset 1/CS1), on the MM cell surface[67]. SLAMF7 is also modestly expressed on NK cells and certain T cells[68,69]. In combination with lenalidomide and dexamethasone, elotuzumab enhances progression-free survival (PFS) in RRMM.
Awwad et al. demonstrated that SLAMF7 was expressed at high levels on CD8+CD28-CD57+ Tregs from MM patients[70]. SLAMF7 levels were also linked with the expression of T cell exhaustion transcription factor signatures and cell surface markers. Elotuzumab specifically depleted SLAMF7+CD8+ T cells in vitro and in vivo through macrophage-dependent ADCP. SLAMF7 may serve as an indicator to identify CD8+ Tregs and anti-SLAMF7 antibodies that enhance anti-myeloma responses.
Isatuximab (Sanofi/Genzyme) targets a specific epitope on the transmembrane glycoprotein CD38, different from that targeted by daratumumab, and inhibits CD38 hydrolase activity[68-75]. CD38 regulates migration and receptor-mediated adhesion by binding to CD31 or hyaluronic acid. Isatuximab induces myeloma death through fragment crystallizable (Fc)-dependent mechanisms, e.g., ADCC, ADCP, and CDC, and direct Fc-independent mechanisms[72]. Isatuximab downregulates constitutive and inducible Tregs resulting in enhancing the anti-myeloma response of other immune cell types[73-75].
Isatuximab was evaluated as monotherapy and demonstrated promising results in a phase I study of 35 RRMM patients as well as a subsequent phase II study alone and in combination with dexamethasone in heavily-pretreated patients[76,77]. Isatuximab added to a pomalidomide-dexamethasone regimen improved PFS, which represents another option to treat lenalidomide- and PI-refractory disease[78]. When combined with pomalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone, isatuximab led to improved PFS and a 40% reduction in the risk of disease progression or death. Patients had an overall response rate (ORR) of 60.4%, compared to 35.3% for patients who only received pomalidomide and dexamethasone. Isatuximab demonstrated a statistically significant increase in TCR clonality after treatment compared to that at treatment initiation, suggesting that isatuximab increases host antitumor immunity.
A recent study assessed isatuximab in heavily-pretreated RRMM patients despite receiving prior anti-CD38 therapy, most patients having been recently exposed to daratumumab combination therapy[79]. Most patients (77%) experienced a response of MR or better with isatuximab. While objective responses were not observed, one patient achieved MR and 17 patients had stable disease as the best overall response[80]. A prospective, randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial compared isatuximab combined with carfilzomib-dexamethasone to carfilzomib-dexamethasone in relapsed MM patients[81]. Isatuximab addition significantly improved PFS and depth of response, representing a new standard of care for this group.
Daratumumab, elotuzumab, and isatuximab act by recruiting immune effectors to enhance cellular cytotoxicity directed against myeloma cells. The anti-myeloma activity of daratumumab and elotuzumab appears independent of the disease stage. These agents may adversely generate allergic-type infusion reactions. Potential complications in serum protein electrophoresis testing and daratumumab cross-reactivity with CD38 present on erythrocytes should be considered. The success of daratumumab and elotuzumab in RRMM has ignited enthusiasm for the development of additional CD38-targeting agents. To note, hypoxia within the BM microenvironment suppresses the maturation of MM cells as well as the expression of CD38 and SLAMF7. While antibody therapy was initially approved for RRMM, there is interest in incorporating monoclonal antibodies into conditioning regimens for NDMM as well.
NUCLEAR EXPORT INHIBITORS
Selinexor (Karyopharm Therapeutics) is a first-in-class orally bioavailable drug that inhibits the nuclear export protein exportin1 (XPO1)[82]. Selinexor has been FDA-approved for use combined with dexamethasone and bortezomib in MM patients previously treated with four prior therapies, including at least two PIs and at least two IMiDs[82,83]. XPO1 overexpression is linked with a worse prognosis in solid tumors and blood cancers[84]. Selinexor also demonstrates an ability to modulate tumor immunology and the surrounding tumor microenvironment. Treatment of B cell lymphomas with selinexor led to increased NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro and selinexor potentiated ADCC-mediated by rituximab and obinutuzumab[85]. NK cells exhibited greater IFN-γ and CD107a expression, both activities associated with NK activation, and lymphoma cells downregulated HLA-E, which binds the inhibitory NKG2A receptor. Zhong et al. demonstrated that selinexor may also downregulate pro-survival signals that originate from the BM microenvironment[86]. Treatment of CLL cells with selinexor blunted protective effects from anti-apoptotic, pro-survival signals from TNF, IL-6, interleukin-4 (IL-4), BAFF, and CD40L in vitro and also blunted anti-apoptotic effects of marrow-derived fibroblast co-culture model. Selinexor may help overcome hypoxia-mediated PI resistance in vitro as well and restore PI sensitivity in vivo[87].
DENOSUMAB
The receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)/RANK signaling system modulates osteoclastogenesis leading to bone resorption[88]. Denosumab (Amgen) is a humanized monoclonal antibody that neutralizes RANKL, inhibits osteoclasts, and decreases the rate of skeletal-related events not only in MM but also in solid tumors[89,90]. Denosumab treatment can inhibit the RANKL/RANL receptor interaction and suppress osteoclastic bone resorption.
BISPHOSPHONATES
Zoledronate (Novartis) and pamidronate (Novartis) are pyrophosphate analogs (bisphosphonates), which demonstrate a high affinity for bone and the capacity to impair osteoclast function as well as anti-angiogenic activities[91-93]. Bisphosphonates inhibit farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase and reduce isoprenylation of Rab, Rac, and Rho. The bisphosphonates are provided as supportive therapy in MM since they are associated with lower rates of vertebral fractures, reduced skeletal-related events, and decreased pain but are associated with an increased risk of jaw osteonecrosis. Nussbaumer et al. showed that zoledronic acid enhanced IFN-γ production by IL-2-primed NK cells in CD14+CD56+ DC-like cell-dependent process that may also require γδ T cells[94].
CAR T CELLS AND BISPECIFIC T CELL ENGAGERS
The adoptive transfer of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-expressing T cells is a transformative approach to improve cancer treatment. B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) displays restricted RNA expression and is selectively expressed by B-lineage cells. BCMA is not detected in healthy tissues and was not detected on human CD34+ HSCs[95]. T cells expressing a CAR-targeting BCMA had substantial activity against heavily-treated RRMM patients[96]. BCMA-targeted CAR T-cell therapies that differ in the costimulatory domain demonstrate efficacy in early-phase trials[97,98]. In 2021, the FDA approved idecabtagene vicleucel (ide-cel, Bristol-Myer Squibb), a BCMA-directed genetically modified autologous T cell therapy, for MM patients that had not responded to > 4 different prior treatments[99]. In 2022, ciltacabtagene autoleucel (cilta-cel), a CAR T-cells with 2 BCMA-targeting single-domain antibodies, was evaluated in RRMM patients with poor prognosis[100]. A single infusion of cilta-cel yielded early, deep, and sustained responses in heavily pretreated patients leading to regulatory approval. CAR T cell therapies have limitations that include life-threatening toxicities, modest antitumor activity, antigen escape, restricted trafficking, and limited tumor infiltration[101-103]. The ECM is composed of fibrous glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans that act as a physical barrier to CAR T cells and prevent their penetration and infiltration of tumors. Matrix-degrading agents that improve immune cell infiltration may enhance the efficacy of CAR-T cells[104-108].
Bispecific T cell engagers (BiTEs) are novel antibody constructs targeting T cells to a tumor antigen. The prototypical BiTE- blinatumumab (Glaxo-Smith Kline) targets CD3 and CD19 to facilitate T cell-mediated killing of relapsed acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) cells [Table 1][109,110]. BiTEs may promote downregulation of their target antigen as a mechanism of immune escape, as evidenced by a metanalysis of ALL patients initially treated with blinatumomab exhibiting increased relapse after CAR T therapy and decreased event-free survival with a trend towards exhibiting more CD19 dim disease. Thus, the development of BiTEs and CAR-T cells with differing target ligands is of clinical interest. Multiple BiTEs have shown promising results in MM including several anti-BCMA/CD3 conjugates as well as talquetamab (Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson), an anti-GPRC5DxCD3 conjugate that targets endogenous T cells to MM cells with a less severe side effect profile than CAR-T cells with step-up outpatient dosing that can be given to the transplant-ineligible patients[111-113]. The immunosuppressive nature of BMSCs poses a significant hurdle to anti-myeloma immunotherapies. Recently, it was shown that MM or AML cell co-culture with the stromal cell lines HS-5 and HS-27a protected the tumor cells from bispecific antibodies that target CD123 and BCMA[114]. The reduction in T cell effector responses was correlated with impaired CD3 redirection cytotoxicity. Cell-cell contact of tumor cells with stromal cells was thought to decrease T cell activation. Agents that inhibit the very late antigen 4 (VLA4) adhesion pathway may be combined with CD3 redirection to reduce stroma-mediated inhibition of T cell activation. The results lend support to inhibiting VLA4 functional activity as well as administering CD3 redirection therapeutics as a combinatorial regimen that enhances antitumor immunity.
CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE PERSPECTIVES
The introduction of IMiDs demonstrated the clinical value of immunotherapeutic approaches for the treatment of MM. However, BM-mediated therapeutic resistance promotes tumor escape and immune evasion that represent obstacles to extending patient outcomes. Recently developed myeloma-directed immunotherapies, e.g., monoclonal antibodies, CAR-T cells, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and BiTEs represent the emerging phase of myeloma care[115-118]. Similar to the mechanisms of resistance observed following the administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy, PIs and IMiDs, novel strategies are needed to prevent or overcome resistance to immunotherapies. Numerous immune cell types, e.g., Tregs, Bregs, MDSCs, macrophages, dysfunctional DCs, MSCs, osteoclasts, as well as the ECM, modulate and suppress T- and NK cell activity. BM-mediated immune exhaustion as well as immune checkpoint proteins on T- and NK cells and their corresponding ligands on MM cells, e.g., PD1/PDL-1, or T cell immunoglobulin and tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (TIGIT) domains, represent additional obstacles[119-121]. Innovative platforms will provide the foundation for the next paradigm shift in myeloma to overcome current limitations and improve high-risk and newly diagnosed patient survival[115-117].
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributionsConceived the article, prepared the figure and table, and wrote the manuscript: Ignatz-Hoover JJ, Driscoll JJ
Made a substantial, direct and intellectual contribution to the work, and approved the final manuscript for publication: Ignatz-Hoover JJ, Driscoll JJ
Availability of data and materialsNot applicable.
Financial support and sponsorshipResearch was supported by NIH R01 (5R01AI139141 to JJD), University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center/Seidman Cancer Center, and the Case Comprehensive Cancer Center.
Conflicts of interestBoth authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participateNot applicable.
Consent for publicationNot applicable.
Copyright© The Author(s) 2022.
REFERENCES
2. Munshi NC, Avet-Loiseau H, Rawstron AC, et al. Association of minimal residual disease with superior survival outcomes in patients with multiple myeloma: a meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol 2017;3:28-35.
3. Available from: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/mulmy.html [Last accessed on 17 May 2022].
4. Available from: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/multiple-myeloma/about/key-statistics.html [Last accessed on 17 May 2022].
5. Cowan AJ, Allen C, Barac A, et al. Global burden of multiple myeloma: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. JAMA Oncol 2018;4:1221-7.
6. Ludwig H, Novis Durie S, Meckl A, Hinke A, Durie B. Multiple myeloma incidence and mortality around the globe; interrelations between health access and quality, economic resources, and patient empowerment. Oncologist 2020;25:e1406-13.
7. Went M, Sud A, Försti A, et al. PRACTICAL consortium. Identification of multiple risk loci and regulatory mechanisms influencing susceptibility to multiple myeloma. Nat Commun 2018;9:3707.
8. Vachon CM, Kyle RA, Therneau TM, et al. Increased risk of monoclonal gammopathy in first-degree relatives of patients with multiple myeloma or monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Blood 2009;114:785-90.
10. Landgren O, Kyle RA, Pfeiffer RM, et al. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) consistently precedes multiple myeloma: a prospective study. Blood 2009;113:5412-7.
11. Kyle RA, Therneau TM, Rajkumar SV, et al. Prevalence of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. N Engl J Med 2006;354:1362-9.
12. Rajkumar SV. Multiple myeloma: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol 2020;95:548-67.
13. Cowan AJ, Green DJ, Kwok M, et al. Diagnosis and management of multiple myeloma: a review. JAMA 2022;327:464-77.
14. Kawano Y, Moschetta M, Manier S, et al. Targeting the bone marrow microenvironment in multiple myeloma. Immunol Rev 2015;263:160-72.
15. Leone P, Solimando AG, Malerba E, et al. Actors on the scene: immune cells in the myeloma niche. Front Oncol 2020;10:599098.
16. Podar K, Chauhan D, Anderson KC. Bone marrow microenvironment and the identification of new targets for myeloma therapy. Leukemia 2009;23:10-24.
17. Moscvin M, Ho M, Bianchi G. Overcoming drug resistance by targeting protein homeostasis in multiple myeloma. Cancer Drug Resist 2021;4:1028-46.
18. Ding L, Morrison SJ. Haematopoietic stem cells and early lymphoid progenitors occupy distinct bone marrow niches. Nature 2013;495:231-5.
19. Son B, Lee S, Youn H, Kim E, Kim W, Youn B. The role of tumor microenvironment in therapeutic resistance. Oncotarget 2017;8:3933-45.
20. Swamydas M, Murphy EV, Ignatz-Hoover JJ, Malek E, Driscoll JJ. Deciphering mechanisms of immune escape to inform immunotherapeutic strategies in multiple myeloma. J Hematol Oncol 2022;15:17.
21. Chen Z, He S, Zilberberg J, Lee W. Pumpless platform for high-throughput dynamic multicellular culture and chemosensitivity evaluation. Lab Chip 2019;19:254-61.
22. Uhl C, Nyirenda T, Siegel DS, Lee WY, Zilberberg J. Natural killer cells activity against multiple myeloma cells is modulated by osteoblast-induced IL-6 and IL-10 production. Heliyon 2022;8:e09167.
23. Madel MB, Ibáñez L, Wakkach A, et al. Immune function and diversity of osteoclasts in normal and pathological conditions. Front Immunol 2019;10:1408.
24. Farrell ML, Reagan MR. Soluble and cell-cell-mediated drivers of proteasome inhibitor resistance in multiple myeloma. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2018;9:218.
25. Markovina S, Callander NS, O’Connor SL, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells from multiple myeloma patients uniquely induce bortezomib resistant NF-kappaB activity in myeloma cells. Mol Cancer 2010;9:176.
26. Moloudizargari M, Abdollahi M, Asghari MH, Zimta AA, Neagoe IB, Nabavi SM. The emerging role of exosomes in multiple myeloma. Blood Rev 2019;38:100595.
27. Roccaro AM, Sacco A, Maiso P, et al. BM mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes facilitate multiple myeloma progression. J Clin Invest 2013;123:1542-55.
28. Wang J, Hendrix A, Hernot S, et al. Bone marrow stromal cell-derived exosomes as communicators in drug resistance in multiple myeloma cells. Blood 2014;124:555-66.
29. Chen T, Moscvin M, Bianchi G. Exosomes in the pathogenesis and treatment of multiple myeloma in the context of the bone marrow microenvironment. Front Oncol 2020;10:608815.
30. Okada T, Hawley RG. Adhesion molecules involved in the binding of murine myeloma cells to bone marrow stromal elements. Int J Cancer 1995;63:823-30.
31. Bunting MD, Vyas M, Requesens M, et al. Extracellular matrix proteins regulate NK cell function in peripheral tissues. Sci Adv 2022;8:eabk3327.
32. Terpos E, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I, Gavriatopoulou M, Dimopoulos MA. Pathogenesis of bone disease in multiple myeloma: from bench to bedside. Blood Cancer J 2018;8:7.
33. Uchiyama H, Barut B, Mohrbacher A, Chauhan D, Anderson K. Adhesion of human myeloma-derived cell lines to bone marrow stromal cells stimulates interleukin-6 secretion. Blood 1993;82:3712-20.
34. Damiano JS, Cress AE, Hazlehurst LA, Shtil AA, Dalton WS. Cell adhesion mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR): role of integrins and resistance to apoptosis in human myeloma cell lines. Blood 1999;93:1658-67.
35. Landowski TH, Olashaw NE, Agrawal D, Dalton WS. Cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) is associated with activation of NF-kappa B (RelB/p50) in myeloma cells. Oncogene 2003;22:2417-21.
36. Wang X, Li C, Ju S, Wang Y, Wang H, Zhong R. Myeloma cell adhesion to bone marrow stromal cells confers drug resistance by microRNA-21 up-regulation. Leuk Lymphoma 2011;52:1991-8.
37. Wallace SR, Oken MM, Lunetta KL, Panoskaltsis-mortari A, Masellis AM. Abnormalities of bone marrow mesenchymal cells in multiple myeloma patients. Cancer 2001;91:1219-30.
38. Feng Y, Wen J, Mike P, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells from myeloma patients support the growth of myeloma stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 2010;19:1289-96.
39. Ria R, Vacca A. Bone marrow stromal cells-induced drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:613.
40. Schlafer D, Shah KS, Panjic EH, Lonial S. Safety of proteasome inhibitors for treatment of multiple myeloma. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2017;16:167-83.
41. Kim HY, Moon JY, Ryu H, et al. Bortezomib inhibits the survival and proliferation of bone marrow stromal cells. Blood Res 2015;50:87-96.
42. Gupta D, Treon SP, Shima Y, et al. Adherence of multiple myeloma cells to bone marrow stromal cells upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor secretion: therapeutic applications. Leukemia 2001;15:1950-61.
43. Roccaro AM, Hideshima T, Raje N, et al. Bortezomib mediates antiangiogenesis in multiple myeloma via direct and indirect effects on endothelial cells. Cancer Res 2006;66:184-91.
44. Holstein SA, McCarthy PL. Immunomodulatory drugs in multiple myeloma: mechanisms of action and clinical experience. Drugs 2017;77:505-20.
45. Quach H, Ritchie D, Stewart AK, et al. Mechanism of action of immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDS) in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2010;24:22-32.
46. Bila J, Katodritou E, Guenova M, et al. Bone marrow microenvironment interplay and current clinical practice in multiple myeloma: a review of the balkan myeloma study group. J Clin Med 2021;10:3940.
47. Stakiw J, Bosch M, Goubran H. A closer look at the bone marrow microenvironment in multiple myeloma. Tumor Microenviron 2018;1:1.
48. Breitkreutz I, Raab MS, Vallet S, et al. Erratum: lenalidomide inhibits osteoclastogenesis, survival factors and bone-remodeling markers in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2008;22:1973-1973.
49. Bolzoni M, Storti P, Bonomini S, et al. Immunomodulatory drugs lenalidomide and pomalidomide inhibit multiple myeloma-induced osteoclast formation and the RANKL/OPG ratio in the myeloma microenvironment targeting the expression of adhesion molecules. Exp Hematol 2013;41:387-97.e1.
50. Corral LG, Haslett PA, Muller GW, et al. Differential cytokine modulation and T cell activation by two distinct classes of thalidomide analogues that are potent inhibitors of TNF-alpha. J Immunol 1999;163:380-6.
51. LeBlanc R, Hideshima T, Catley LP, et al. Immunomodulatory drug costimulates T cells via the B7-CD28 pathway. Blood 2004;103:1787-90.
52. Henry JY, Labarthe MC, Meyer B, Dasgupta P, Dalgleish AG, Galustian C. Enhanced cross-priming of naive CD8+ T cells by dendritic cells treated by the IMiDs® immunomodulatory compounds lenalidomide and pomalidomide. Immunology 2013;139:377-85.
53. Chang DH, Liu N, Klimek V, et al. Enhancement of ligand-dependent activation of human natural killer T cells by lenalidomide: therapeutic implications. Blood 2006;108:618-21.
54. Zhu D, Corral LG, Fleming YW, Stein B. Immunomodulatory drugs Revlimid (lenalidomide) and CC-4047 induce apoptosis of both hematological and solid tumor cells through NK cell activation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2008;57:1849-59.
55. Galustian C, Meyer B, Labarthe MC, et al. The anti-cancer agents lenalidomide and pomalidomide inhibit the proliferation and function of T regulatory cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2009;58:1033-45.
56. Görgün G, Calabrese E, Soydan E, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of lenalidomide and pomalidomide on interaction of tumor and bone marrow accessory cells in multiple myeloma. Blood 2010;116:3227-37.
57. Tamura H, Ishibashi M, Yamashita T, et al. Marrow stromal cells induce B7-H1 expression on myeloma cells, generating aggressive characteristics in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2013;27:464-72.
58. Liu J, Hamrouni A, Wolowiec D, et al. Plasma cells from multiple myeloma patients express B7-H1 (PD-L1) and increase expression after stimulation with IFN-{gamma} and TLR ligands via a MyD88-, TRAF6-, and MEK-dependent pathway. Blood 2007;110:296-304.
59. Suzuki K, Nishiwaki K, Yano S. Treatment strategies considering micro-environment and clonal evolution in multiple myeloma. Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:215.
60. Lokhorst HM, Plesner T, Laubach JP, et al. Targeting CD38 with daratumumab monotherapy in multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2015;373:1207-19.
61. Chari A, Martinez-Lopez J, Mateos MV, et al. Daratumumab plus carfilzomib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2019;134:421-31.
62. Dimopoulos MA, Oriol A, Nahi H, et al. POLLUX Investigators. Daratumumab, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2016;375:1319-31.
63. Palumbo A, Chanan-Khan A, Weisel K, et al. CASTOR Investigators. Daratumumab, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2016;375:754-66.
64. Voorhees PM, Kaufman JL, Laubach J, et al. Daratumumab, lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone for transplant-eligible newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: the GRIFFIN trial. Blood 2020;136:936-45.
65. Krejcik J, Casneuf T, Nijhof IS, et al. Daratumumab depletes CD38+ immune regulatory cells, promotes T-cell expansion, and skews T-cell repertoire in multiple myeloma. Blood 2016;128:384-94.
66. Ghose J, Viola D, Terrazas C, et al. Daratumumab induces CD38 internalization and impairs myeloma cell adhesion. Oncoimmunology 2018;7:e1486948.
67. Trudel S, Moreau P, Touzeau C. Update on elotuzumab for the treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma: patients’ selection and perspective. Onco Targets Ther 2019;12:5813-22.
68. Ackley J, Ochoa MA, Ghoshal D, Roy K, Lonial S, Boise LH. Keeping myeloma in check: the past, present and future of immunotherapy in multiple myeloma. Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:4787.
69. Hsi ED, Steinle R, Balasa B, et al. CS1, a potential new therapeutic antibody target for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:2775-84.
70. Awwad MHS, Mahmoud A, Bruns H, et al. Selective elimination of immunosuppressive T cells in patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2021;35:2602-15.
72. Zhu C, Song Z, Wang A, et al. Isatuximab acts through Fc-dependent, independent, and direct pathways to kill multiple myeloma cells. Front Immunol 2020;11:1771.
73. Moreno L, Perez C, Zabaleta A, et al. The mechanism of action of the anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody isatuximab in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2019;25:3176-87.
74. Tai YT, Anderson KC. Targeting CD38 alleviates tumor-induced immunosuppression. Oncotarget 2017;8:112166-7.
75. Deckert J, Wetzel MC, Bartle LM, et al. SAR650984, a novel humanized CD38-targeting antibody, demonstrates potent antitumor activity in models of multiple myeloma and other CD38+ hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 2014;20:4574-83.
76. Martin TG, Hsu K, Strickland SA, et al. A phase I trial of SAR650984, a CD38 monoclonal antibody, in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2014;32:Suppl:8532.
77. Dimopoulos MA, Bringhen S, Anttila P, et al. Results from a phase II study of isatuximab as a single agent and in combination with dexamethasone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2018;132:155-155.
78. Mikhael J, Belhadj-Merzoug K, Hulin C, et al. A phase 2 study of isatuximab monotherapy in patients with multiple myeloma who are refractory to daratumumab. Blood Cancer J 2021;11:89.
79. Becnel MR, Horowitz SB, Thomas SK, et al. Descriptive analysis of isatuximab use following prior daratumumab in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Blood 2020;136:20-1.
80. Mikhael J, Belhadj-Merzoug K, Hulin C, et al. A phase 2 study of isatuximab monotherapy in patients with multiple myeloma who are refractory to daratumumab. Blood Cancer J 2021;11:89.
81. Moreau P, Dimopoulos M, Mikhael J, et al. Isatuximab, carfilzomib, and dexamethasone in relapsed multiple myeloma (IKEMA): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. The Lancet 2021;397:2361-71.
82. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-selinexor-refractory-or-relapsed-multiple-myeloma [Last accessed on 17 May 2022].
83. Grosicki S, Simonova M, Spicka I, et al. Once-per-week selinexor, bortezomib, and dexamethasone versus twice-per-week bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with multiple myeloma (BOSTON): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. The Lancet 2020;396:1563-73.
84. Deng M, Zhang M, Xu-Monette ZY, et al. XPO1 expression worsens the prognosis of unfavorable DLBCL that can be effectively targeted by selinexor in the absence of mutant p53. J Hematol Oncol 2020;13:148.
85. Fisher JG, Walker CJ, Doyle AD, et al. Selinexor enhances NK cell activation against malignant B cells via downregulation of HLA-E. Front Oncol 2021;11:785635.
86. Zhong Y, El-Gamal D, Dubovsky JA, et al. Selinexor suppresses downstream effectors of B-cell activation, proliferation and migration in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Leukemia 2014;28:1158-63.
87. Muz B, Azab F, de la Puente P, Landesman Y, Azab AK. Selinexor overcomes hypoxia-induced drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Transl Oncol 2017;10:632-40.
88. Cheng ML, Fong L. Effects of RANKL-targeted therapy in immunity and cancer. Front Oncol 2014;3:329.
89. Terpos E, Raje N, Croucher P, et al. Denosumab compared with zoledronic acid on PFS in multiple myeloma: exploratory results of an international phase 3 study. Blood Adv 2021;5:725-36.
90. Raje N, Terpos E, Willenbacher W, et al. Denosumab versus zoledronic acid in bone disease treatment of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: an international, double-blind, double-dummy, randomised, controlled, phase 3 study. The Lancet Oncology 2018;19:370-81.
91. Mhaskar R, Djulbegovic B. Bisphosphonates for patients diagnosed with multiple myeloma. JAMA 2018;320:1483-4.
92. Berbari HE, Kumar SK. Initial therapeutic approaches to patients with multiple myeloma. Adv Ther 2021;38:3694-711.
93. Pozzi S, Raje N. The role of bisphosphonates in multiple myeloma: mechanisms, side effects, and the future. Oncologist 2011;16:651-62.
94. Nussbaumer O, Gruenbacher G, Gander H, Thurnher M. DC-like cell-dependent activation of human natural killer cells by the bisphosphonate zoledronic acid is regulated by γδ T lymphocytes. Blood 2011;118:2743-51.
95. Carpenter RO, Evbuomwan MO, Pittaluga S, et al. B-cell maturation antigen is a promising target for adoptive T-cell therapy of multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 2013;19:2048-60.
96. Brudno JN, Maric I, Hartman SD, et al. T cells genetically modified to express an anti-B-cell maturation antigen chimeric antigen receptor cause remissions of poor-prognosis relapsed multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2018;36:2267-80.
97. Shah N, Chari A, Scott E, Mezzi K, Usmani SZ. B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in multiple myeloma: rationale for targeting and current therapeutic approaches. Leukemia 2020;34:985-1005.
98. Rodriguez-Garcia A, Palazon A, Noguera-Ortega E, Powell DJ Jr, Guedan S. CAR-T cells hit the tumor microenvironment: strategies to overcome tumor escape. Front Immunol 2020;11:1109.
99. Munshi NC, Anderson LD Jr, Shah N, et al. Idecabtagene vicleucel in relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 2021;384:705-16.
100. Berdeja JG, Madduri D, Usmani SZ, et al. Ciltacabtagene autoleucel, a B-cell maturation antigen-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (CARTITUDE-1): a phase 1b/2 open-label study. The Lancet 2021;398:314-24.
101. Rafiq S, Hackett CS, Brentjens RJ. Engineering strategies to overcome the current roadblocks in CAR T cell therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2020;17:147-67.
102. Sterner RC, Sterner RM. CAR-T cell therapy: current limitations and potential strategies. Blood Cancer J 2021;11:69.
103. Franssen LE, Mutis T, Lokhorst HM, van de Donk NWCJ. Immunotherapy in myeloma: how far have we come? Ther Adv Hematol 2019;10:2040620718822660.
104. Holthof LC, Mutis T. Challenges for immunotherapy in multiple myeloma: bone marrow microenvironment-mediated immune suppression and immune resistance. Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:988.
105. Eikenes L, Bruland ØS, Brekken C, Davies Cde L. Collagenase increases the transcapillary pressure gradient and improves the uptake and distribution of monoclonal antibodies in human osteosarcoma xenografts. Cancer Res 2004;64:4768-73.
106. Hingorani SR, Harris WP, Beck JT, et al. Phase Ib study of PEGylated recombinant human hyaluronidase and gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2016;22:2848-54.
107. Hingorani SR, Zheng L, Bullock AJ, et al. HALO 202: Randomized phase II study of PEGPH20 plus nab-paclitaxel/gemcitabine versus nab-paclitaxel/gemcitabine in patients with untreated, metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2018;36:359-66.
108. Jacobetz MA, Chan DS, Neesse A, et al. Hyaluronan impairs vascular function and drug delivery in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Gut 2013;62:112-20.
109. Rodríguez-García A, Giménez-Alejandre M, Rojas JJ, et al. Safety and efficacy of VCN-01, an oncolytic adenovirus combining fiber HSG-binding domain replacement with RGD and hyaluronidase expression. Clin Cancer Res 2015;21:1406-18.
110. Braig F, Brandt A, Goebeler M, et al. Resistance to anti-CD19/CD3 BiTE in acute lymphoblastic leukemia may be mediated by disrupted CD19 membrane trafficking. Blood 2017;129:100-4.
111. Xu X, Sun Q, Liang X, et al. Mechanisms of relapse after CD19 CAR T-Cell therapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its prevention and treatment strategies. Front Immunol 2019;10:2664.
112. Berdeja JG, Krishnan AY, Oriol A, et al. Updated results of a phase 1, first-in-human study of talquetamab, a G protein-coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D) × CD3 bispecific antibody, in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (MM). JCO 2021;39:8008-8008.
113. van de Donk NWCJ, Minnema MC, Berdeja JG, et al. P10: talquetamab, a G protein-coupled receptor family C group 5 member D X CD3 bispecific antibody, in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (rrmm): updated phase 1 results from monumental-1. HemaSphere 2022;6:16-7.
114. Smith EL, Harrington K, Staehr M, et al. GPRC5D is a target for the immunotherapy of multiple myeloma with rationally designed CAR T cells. Sci Transl Med 2019;11:eaau7746.
115. Nair-Gupta P, Rudnick SI, Luistro L, et al. Blockade of VLA4 sensitizes leukemic and myeloma tumor cells to CD3 redirection in the bone marrow microenvironment. Blood Cancer J 2020;10:65.
116. Mikkilineni L, Kochenderfer JN. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies for multiple myeloma. Blood 2017;130:2594-602.
117. Goldsmith SR, Vij R. Evolving paradigms of therapy for multiple myeloma: state of the art and future directions. JCO Oncol Pract 2021;17:415-8.
118. Mohan M, Hari P, Dhakal B. Immunotherapy in multiple myeloma-time for a second major paradigm shift. JCO Oncol Pract 2021;17:405-13.
120. Görgün GT, Whitehill G, Anderson JL, et al. Tumor-promoting immune-suppressive myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the multiple myeloma microenvironment in humans. Blood 2013;121:2975-87.
121. Ramachandran IR, Martner A, Pisklakova A, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells regulate growth of multiple myeloma by inhibiting T cells in bone marrow. J Immunol 2013;190:3815-23.
122. Uckun FM. Overcoming the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in multiple myeloma. Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:2018.
123. Verkleij CPM, Broekmans MEC, van Duin M, et al. Preclinical activity and determinants of response of the GPRC5DxCD3 bispecific antibody talquetamab in multiple myeloma. Blood Adv 2021;5:2196-215.
124. Topp MS, Duell J, Zugmaier G, et al. Anti-B-cell maturation antigen bite molecule AMG 420 induces responses in multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol 2020;38:775-83.
125. Topp MS, Duell J, Zugmaier G, et al. Treatment with AMG 420, an Anti-B-Cell Maturation Antigen (BCMA) Bispecific T-Cell Engager (BiTE®) antibody construct, induces minimal residual disease (MRD) negative complete responses in relapsed and/or refractory (R/R) multiple myeloma (MM) patients: results of a first-in-human (FIH) phase I dose escalation study. Blood 2018;132:1010.
Cite This Article
Export citation file: BibTeX | RIS
OAE Style
Ignatz-Hoover JJ, Driscoll JJ. Therapeutics to harness the immune microenvironment in multiple myeloma. Cancer Drug Resist 2022;5:647-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2022.23
AMA Style
Ignatz-Hoover JJ, Driscoll JJ. Therapeutics to harness the immune microenvironment in multiple myeloma. Cancer Drug Resistance. 2022; 5(3): 647-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2022.23
Chicago/Turabian Style
Ignatz-Hoover, James J., James J. Driscoll. 2022. "Therapeutics to harness the immune microenvironment in multiple myeloma" Cancer Drug Resistance. 5, no.3: 647-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2022.23
ACS Style
Ignatz-Hoover, JJ.; Driscoll JJ. Therapeutics to harness the immune microenvironment in multiple myeloma. Cancer Drug Resist. 2022, 5, 647-61. http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/cdr.2022.23
About This Article
Special Issue
Copyright
Data & Comments
Data
 Cite This Article 10 clicks
Cite This Article 10 clicks














Comments
Comments must be written in English. Spam, offensive content, impersonation, and private information will not be permitted. If any comment is reported and identified as inappropriate content by OAE staff, the comment will be removed without notice. If you have any queries or need any help, please contact us at support@oaepublish.com.